Newsletter link is not currently active
Physics Electric and Magnetic Fields
Physics Electric and Magnetic Fields
HS PS3-5
HS PS3-5
Biology
LS2-1 Factors Affecting Ecosystems
Page Under Construction
Newsletter link is not currently active
LS1 6 Atoms from Sugar forming Macromolecules
Project Zero THINKING ROUTINES
HS-LS1-6. Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for how carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen from sugar molecules may combine with other elements to form amino acids and/or other large carbon-based molecules.
[Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on using evidence from models and simulations to support explanations.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the details of the specific chemical reactions or identification of macromolecules.]
Inquiry science
Printable activity
Matter and Organic Chemistry Go To Lesson 2 CK-12
On-line activity
LAB activities follow safety guidelines linked above
and in the activity
Lab #1 Organic molecules and nutrition labels and write formulas for one example of each food class LHSblogs
Lab #2 Materials in our food BSCS
EXTENSION material for the curious
Building blocks of life’s building blocks come from starlight (CH, CH+, C+) NASA Explore
A gallon of gasoline (6.3.lb) produces 20 lb of CO2 NASA Climate Kids
.CELL METABOLISM
-
Molecular biology explains living processes in terms of the chemical substances involved.
-
Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds forming stable compounds
-
Life is based on carbon compounds including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids.
-
Metabolism describes all the enzyme-catalysed reactions in an organism.
-
Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions.
-
Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers.
Aerospace CONNECTIONS:
Applications and examples
The Fast Carbon Cycle NASA Explore
NASA’s Curiosity takes inventory on key life ingredient on Mars (Total carbon) NASA Explore
Hydrogen recovery by methane pyrolysis to elemental carbon NASA
Ingredients for life on a Saturn Moon The Columbian
Organics on Mars Astronomy magazine and NASA
Making Protein Crystals in Space
There are 100,000 different proteins in the human body
Studying the structures with X-ray crystallography or neutron diffraction help scientists learn more about them--perhaps to develop medicines, or synthesize them artificially
Better diffraction results occur with better crystals and growing crystals in space in a microgravity environment gets better crystals


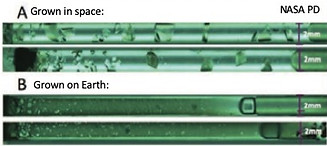


Crystals of pyrophosphatase grown for 6 months--one sample in Space, one on Earth

The same crystals seen in polarized light

The Protein Crystallization Diagnostics Facility
Find out more about crystals in Space: Macromolecular crystallization in space NASA
High Density Protein Crystal Growth. NASA University of Alabama PD
Protein Crystal Malic Enzyme
More about the body's macromolecules
Carbohydrates, Proteins and Lipids
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Carbohydrates are complex sugar molecules that are made up of long chains of monosaccharide units known as polysaccharide molecules.
Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
Carbohydrates provide the energy required by all cells in the body. Cells use glucose in the respiration process to carry out metabolic activities

Monosaccharide
(CH2O)n

Disaccharide
examples sucrose and galactose

Polysaccharide
examples starch and cellulose
Function of carbohydrates:
Digestive enzymes break down polysaccharides (ex. starch) so they can be absorbed by the body. Monosaccharides ex. glucose and fructose release energy from cellular respiration--releasing energy for cell processes
Carbohydrates are precursors for metabolic reactions including the synthesis of macromolecules such as fats, nucleic acids, and amino acids
Glycogen is a storage form of carbohydrates–-energy reserves in liver and muscles
Cellulose provides the support structure for plants
Proteins
Proteins are chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and folded into a specific 3D structure that also have crosslinks, such as disulphide bridges, between specific amino acids to hold it in shape.
>20 amino acids are required for good health, our bodies can only make 14 of these essential amino acids, thus the others essential amino acids can only be obtained from food



Proteins maintain, build and repair body tissues.
